With the popularization of new energy electric vehicles, electric vehicle charging stations, as a newly emerging electricity metering device, are involved in electricity trade settlement, whether DC or AC. Mandatory metering verification of electric vehicle charging stations can ensure public safety, improve product quality, and promote the rapid development of new energy vehicles.
Types of Charging Stations
When new energy vehicles use electric car charging stations for energy replenishment, according to the charging power, charging time, and the type of current output from the charging station, charging methods can be divided into two types: DC fast charging and AC slow charging.
1. DC Fast Charging (DC Fast Charging Station)
DC fast charging refers to high-power DC charging. It uses the charging station interface to directly convert AC power from the power grid into DC power, which is then delivered to the battery for charging. Electric vehicles can be charged to 80% in as little as half an hour. In most cases, the power can reach over 40kW.
2. AC Slow Charging (AC Charging Pile)
AC charging uses the AC charging station interface to input AC power from the power grid into the electric vehicle’s charger, which then converts it into DC power before delivering it to the battery for charging. Most car models require 1-3 hours to fully charge their batteries. Slow charging power is mostly between 3.5kW and 44kW.
Regarding charging stations:
1. Nameplate Markings:
The charging station nameplate should include the following markings:
—Name and model; —Manufacturer’s name;
—Standard upon which the product is based;
—Serial number and year of manufacture;
—Maximum voltage, minimum voltage, minimum current, and maximum current;
—Constant;
—Accuracy class;
—Unit of measurement (the unit of measurement can be displayed on the screen).
2. Charging Station Appearance:
In addition to the label, before using the charger, check the charging station’s appearance:
—Are the markings safe and the lettering clear?
—Are there any obvious damages?
—Are there measures to prevent authorized personnel from inputting data or operating the system?
—Do the display digits meet the requirements?
—Are the basic functions normal?
3. Charging Capacity: The EV charging station should be able to display the charging capacity, with at least 6 digits (including at least 3 decimal places).
4. Verification Cycle: The verification cycle for charging stations generally does not exceed 3 years.
How to Distinguish Between Fast Charging and Slow Charging
1. Different Charging Ports
Almost every electric vehicle has two charging ports, and these two ports are different. A slow charging port consists of four output ports (L1, L2, L3, N), a ground port (PE), and two signal ports (CC, CP). A fast charging port consists of DC+, DC-, S+, S-, CC1, CC2, A+, A-, and PE.
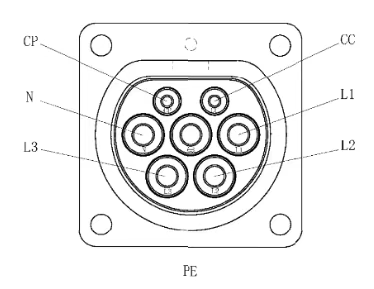
2. Different Charging Station Sizes
Because the current conversion for fast charging is completed on the charging station, fast charging stations are larger than slow charging stations, and the charging gun is also heavier.

3. Check the nameplate.
Every qualified charging station will have a nameplate. We can check the rated power of the charging station through the nameplate, and we can also quickly identify the type of charging station through the data on the nameplate.
Post time: Nov-13-2025





