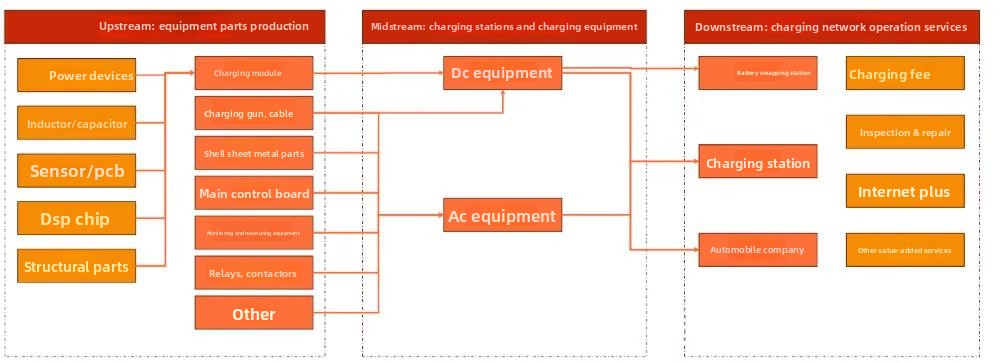
The charging industry chain: core equipment manufacturing and operation are the core links.
• The charging pile industry comprises three main segments: upstream (ev charging pile equipment manufacturers), midstream (electric car charging station manufacturing), and downstream (charging operators).
• Upstream: Primarily suppliers of ev charging pile equipment components and parts. Components include charging modules, power distribution and filtering equipment, fuses, circuit breakers, cables, and billing equipment. Charging modules further include power devices, magnetic materials, and capacitors.
• Midstream: Primarily manufacturers of complete electric vehicle charging station systems. Participants include electrical equipment companies, third-party charging pile manufacturers, and home appliance companies.
• Downstream: Primarily overseas charging service operators. These operators can be categorized into three main types: specialized operators, power grid/energy companies, and vehicle manufacturers.
Charging Industry Chain Map
Upstream equipment: low barriers to entry, high homogeneity, fragmented market.
• The upstream charging equipment industry has low entry barriers, high product homogeneity, and intense competition. Currently, there are over 300 companies in China producing electric car charging pile equipment, resulting in a highly fragmented market with limited bargaining power and low profit margins for upstream companies.
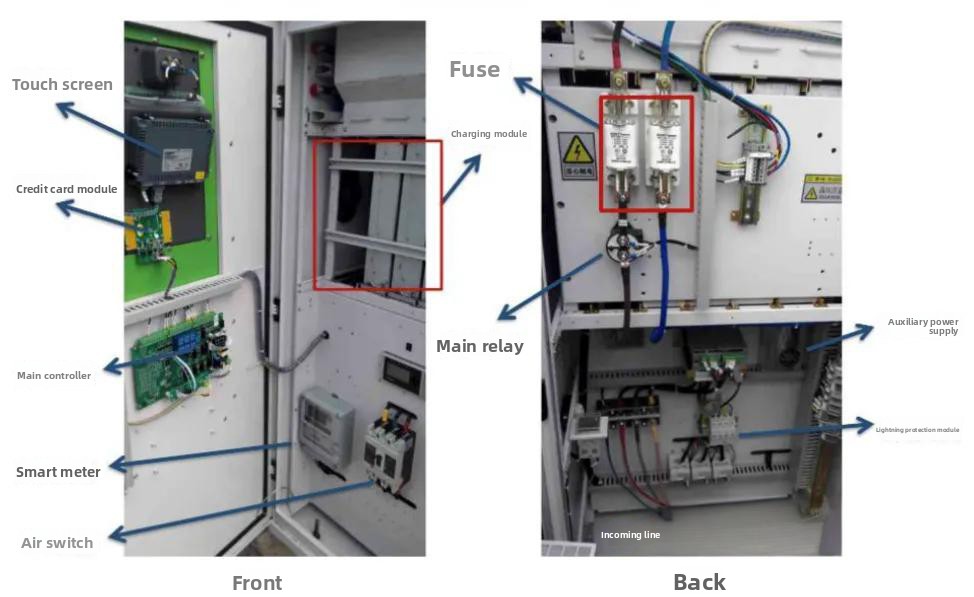
• DC charging piles consist of power units, control units, metering units, charging interfaces, power supply interfaces, and human-machine interfaces. The power unit refers to the DC charging module, and the control unit refers to the ev charging station controller. These two components constitute the core technology, and structural design is also a key aspect of the overall pile’s reliability.
• DC charging pile power: Modular power combinations are used, with individual charging modules offering power outputs of 15kW, 20kW, 30kW, 40kW, etc. Therefore, DC charging station output power is generally 30kW, 40KW, 60kW, 80KW, 120kW, 240kW, 360kW, 480kW, etc. According to the China Charging Alliance, current DC charging pile power is generally above 60kW.
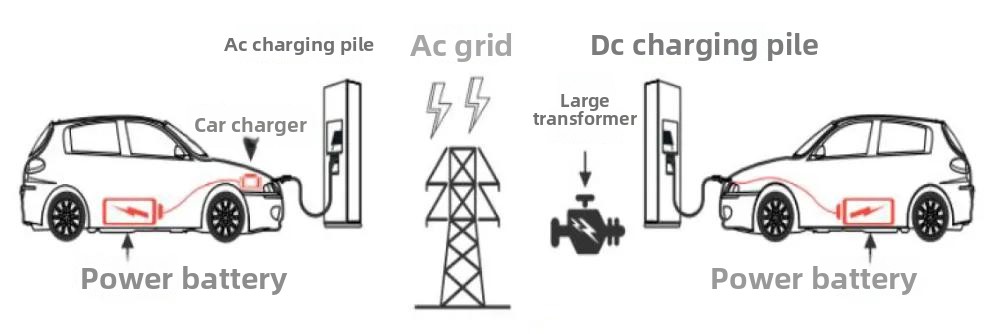
• AC charging piles do not have charging modules; they only provide power output and require connection to an on-board charger. AC charging stations connect to the vehicle’s onboard charger, directly converting AC input (220V/380V) into high-voltage DC output to charge electric vehicles. They primarily function as power control systems.
• AC charging stations have lower power output and slower charging speeds. They are available in single-phase (mainly 7kW) and three-phase (mainly 40kW) configurations. Due to the power limitations of the onboard charger, they generally have lower power and slower charging speeds. Common power outputs include 3.5kW, 7kW, 11kW, 21kW, and 40kW. In the market, single-phase AC charging piles are primarily 7kW, and three-phase stations are primarily 40kW. DC charging piles, on the other hand, convert AC to DC output, directly charging the battery. They offer higher power and faster charging speeds.
DC charging pile structure
Schematic diagrams of AC charging and DC charging
Post time: Dec-12-2025